Quantitative evaluation of iron content in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder
Abstract
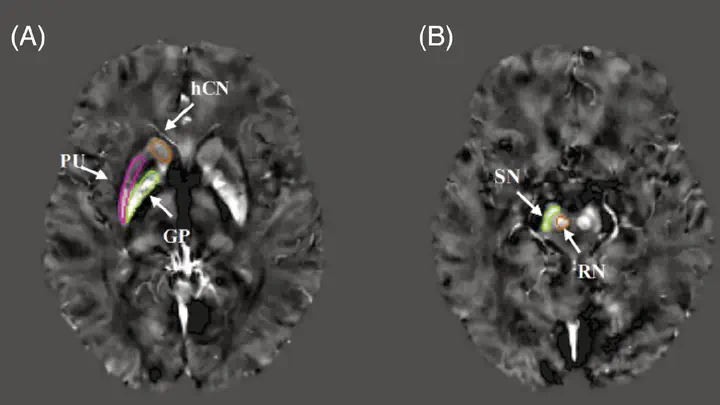
Idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder is an early sign of neurodegenerative disease. This study aimed to quantitatively evaluate iron content in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder patients using quantitative susceptibility mapping and to examine the potential of this technique to identify the prodromal stage of α-synucleinopathies. Twenty-five idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder patients, 32 Parkinson’s disease patients, and 50 healthy controls underwent quantitative susceptibility mapping. The mean magnetic susceptibility values within the bilateral substantia nigra, globus pallidus, red nucleus, head of the caudate nucleus, and putamen were calculated and compared among groups. The relationships between the values and the clinical features of idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease were measured using correlation analysis. Idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder patients had elevated iron in the bilateral substantia nigra compared with healthy controls. Parkinson’s disease patients had increased iron in the bilateral substantia nigra, globus pallidus, and left red nucleus compared with healthy controls and had elevated iron levels in the bilateral substantia nigra compared with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder patients. Mean magnetic susceptibility values were positively correlated with disease duration in the left substantia nigra in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder patients. Quantitative susceptibility mapping can detect increased iron in the substantia nigra in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder, which becomes more significant as the disorder progresses. This technique has the potential to be an early objective neuroimaging marker for detecting α-synucleinopathies.